Inflammation 101: What It Means for Your Health and How to Manage It
Share
Inflammation is a natural and essential process in the body. It’s the way your immune system defends itself against injury, infection, or harmful substances. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can quietly wreak havoc on your overall health and contribute to a host of diseases.
Understanding the connection between inflammation and your well-being is key to taking proactive steps to support your body.
What Is Inflammation?
Inflammation is your body’s defense mechanism. It’s how your immune system responds to perceived threats, such as infections or injuries. Acute inflammation is short-term and beneficial—it helps the body heal and recover. For example, redness and swelling around a cut are signs of your immune system at work.
However, chronic inflammation is a different story. This low-grade, persistent inflammation occurs when the immune system remains active for extended periods, even when no immediate threat is present. It can damage healthy cells, tissues, and organs, leading to long-term health issues.
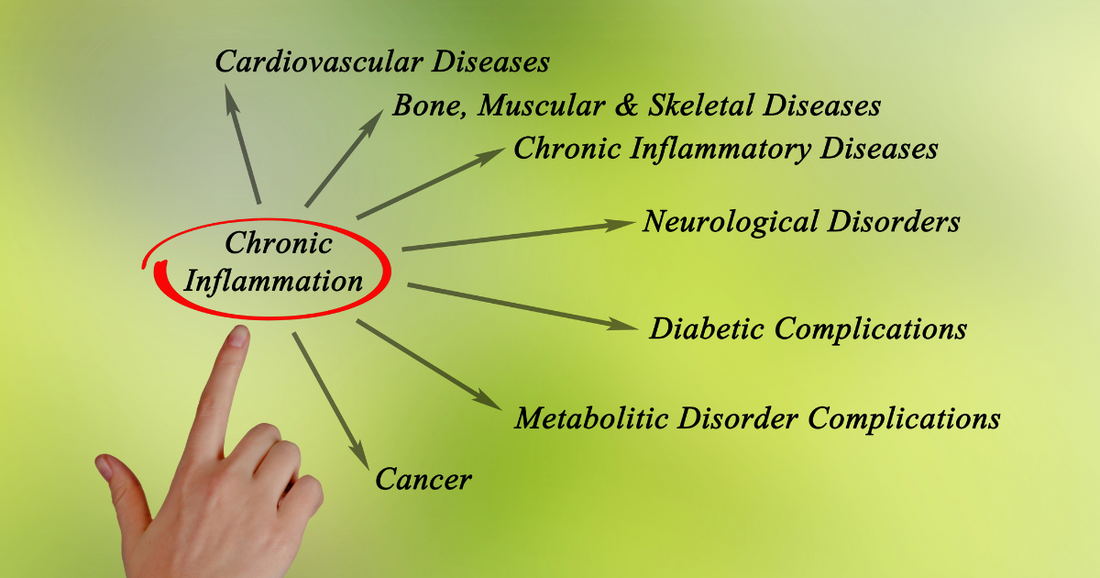
The Impact of Chronic Inflammation on Health
Chronic inflammation has been linked to numerous health conditions, including:
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Inflammation can contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, leading to atherosclerosis. This increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2. Autoimmune Disorders
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis are marked by chronic inflammation, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues.
3. Diabetes
Inflammation plays a role in insulin resistance, a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes.
4. Digestive Disorders
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, causing significant digestive discomfort and damage.
5. Cancer
Persistent inflammation can create an environment that promotes the growth of cancer cells.
6. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Inflammation in the brain has been associated with Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative conditions.
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
Several factors can trigger or exacerbate chronic inflammation:
- Diet: High intake of sugar, processed foods, and trans fats.
- Stress: Prolonged stress can keep your immune system in a state of hyperactivity.
- Environmental Toxins: Pollution, chemicals, and allergens can trigger an inflammatory response.
- Poor Gut Health: Imbalances in gut bacteria can promote inflammation throughout the body.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, lack of sleep, and sedentary behavior can all contribute to inflammation.
Signs of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation doesn’t always produce obvious symptoms. However, subtle signs may include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Body aches or joint pain
- Digestive issues, like bloating or constipation
- Skin problems, such as eczema or acne
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
How to Reduce Inflammation Naturally
Reducing chronic inflammation is essential for promoting overall health and preventing disease. Here are some practical steps you can take:
1. Eat an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that fight inflammation:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants and fiber (e.g., berries, leafy greens).
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids from fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds.
- Spices: Turmeric, ginger, and garlic have powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
Avoid inflammatory foods like refined sugar, processed meats, and trans fats.
2. Prioritize Gut Health
A healthy gut supports a healthy immune system. Probiotics (found in fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi) and prebiotics (found in foods like onions and garlic) are great for balancing gut bacteria.
3. Manage Stress
Chronic stress contributes to inflammation. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
4. Stay Active
Regular exercise helps reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days of the week.
5. Get Quality Sleep
Poor sleep is linked to increased inflammation. Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night by creating a calming bedtime routine.
6. Use Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs and supplements can be incredibly helpful in reducing inflammation and supporting the body’s natural healing processes. Many herbs have powerful anti-inflammatory properties that not only target inflammation but also support joint, digestive, and overall health. Here are some herbs that can help:
- Turmeric (Curcumin): One of the most well-known anti-inflammatory herbs, turmeric contains curcumin, a compound that has been shown to reduce inflammation and support joint health.
- Ginger: Ginger is another powerful anti-inflammatory herb that helps reduce swelling and soothes digestive discomfort, making it ideal for both inflammation and digestion.
- Boswellia (Frankincense): Often used in traditional medicine, Boswellia is known for its ability to reduce inflammation in the joints, particularly in conditions like arthritis.
- Willow Bark: Known as nature’s aspirin, willow bark contains salicin, which helps reduce pain and inflammation, particularly in the case of headaches and joint pain.
- Holy Basil (Tulsi): Holy Basil is revered for its ability to reduce stress-induced inflammation while also supporting the body’s immune system and reducing anxiety.
- Devil’s Claw: Often used for its anti-inflammatory effects, especially for musculoskeletal issues, Devil’s Claw is effective for relieving joint pain and inflammation.
- Cayenne Pepper (Capsaicin): The compound capsaicin in cayenne pepper can help reduce inflammation in the body by increasing circulation and relieving muscle pain.
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants, green tea contains compounds like EGCG that have been shown to reduce inflammation and protect against chronic disease.
- Chamomile: This calming herb has anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe the digestive system and reduce irritation in the body.
- Nettle: Nettle has natural anti-inflammatory properties and can be especially helpful for reducing joint pain, making it beneficial for those with arthritis or other inflammatory conditions.
Incorporating these herbs into your daily routine, whether through teas, capsules, or tinctures, can provide significant support in managing and reducing inflammation. Make sure to consult with a healthcare professional to find the right combination of herbs for your specific needs.
7. Avoid Toxins
Minimize exposure to pollutants, pesticides, and chemicals by choosing natural products, eating organic foods, and using air purifiers.
Inflammation is both a friend and a foe. While acute inflammation is vital for healing, chronic inflammation can lead to serious health problems. By understanding the connection between inflammation and overall health, you can take proactive steps to reduce inflammation and support your body’s natural balance.
Your journey to wellness starts with small, intentional choices that nurture your body and mind. Embrace these strategies, and you’ll be on your way to living a healthier, inflammation-free.
